
Education&ScienceEducational Article
Seasonality of common respiratory viruses: Analysis of nationwide time-series data
November 2024
Authors: Tai Joon An, Jangwon Lee, Myoungin Shin, Chin Kook Rhee
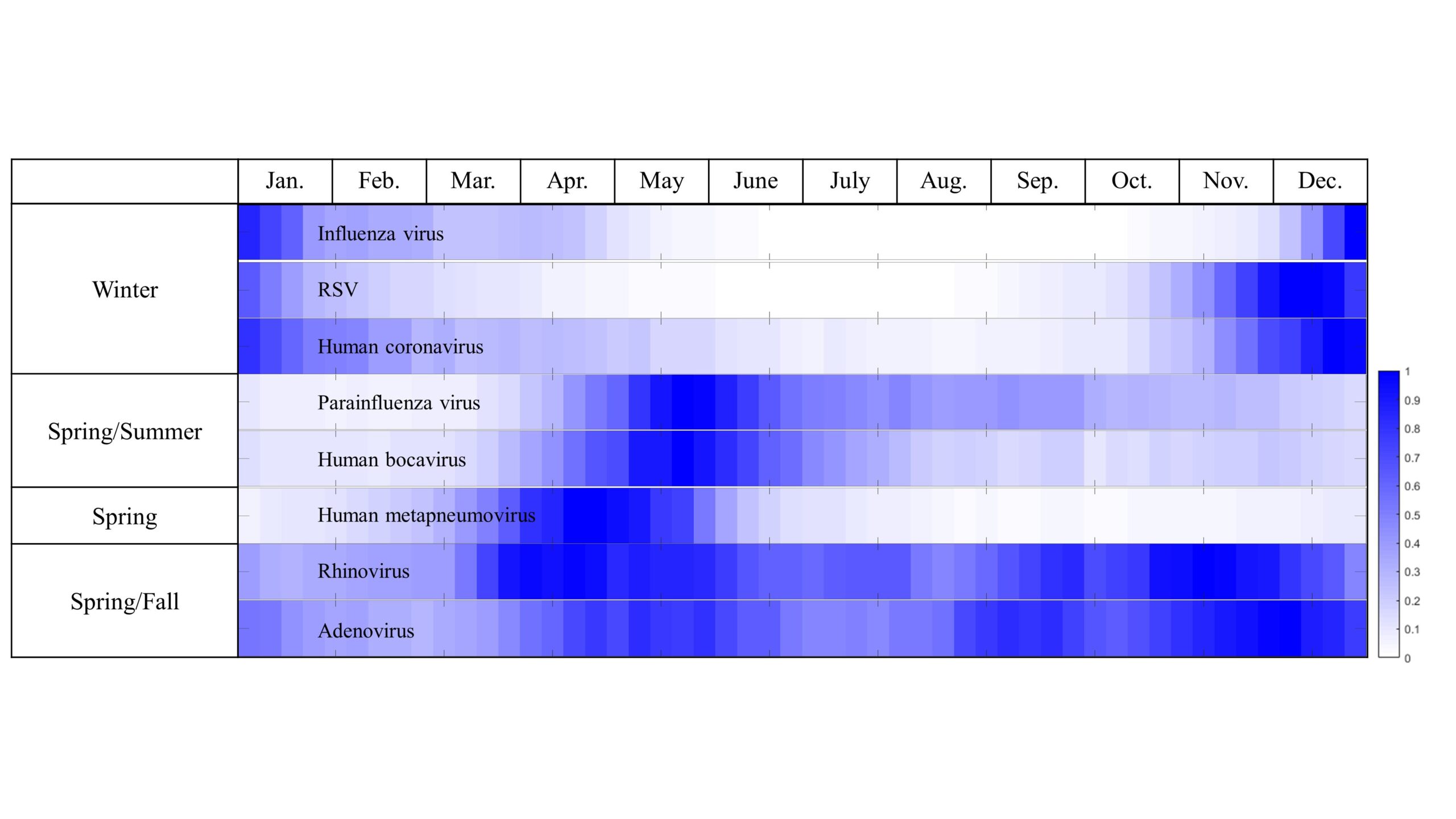
Comment by Mark Lavercombe: The period of each year in which a particular respiratory virus is most active depends on environmental (temperature, humidity and sunlight) and social (school and work periods, major events and public policy) factors, meaning local data is critical to prediction of infections. In this paper, the authors use statistical methods including Dynamic time warping and Seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average to examine the periodicity of eight respiratory viruses in South Korea, both before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. In this population, rhinovirus and adenovirus infections appear throughout the year, while other viruses have a predictable monthly distribution.



