
Education&ScienceEducational Article
Safety and efficacy of a novel transbronchial radiofrequency ablation system for lung tumours: One year follow-up from the first multi-centre large-scale clinical trial (BRONC-RFII)
January 2025
Authors: Changhao Zhong, Enguo Chen, Zhuquan Su, Difei Chen, Feng Wang, Xiaoping Wang, Guangnan Liu, Xiaoju Zhang, Fengming Luo, Nan Zhang, Hongwu Wang, Longyu Jin, Fa Long, Chunfang Liu, Shiman Wu, Qing Geng, Xiang Wang, Chunli Tang, Ruchong Chen, Felix J. F. Herth, Jiayuan Sun, Shiyue Li
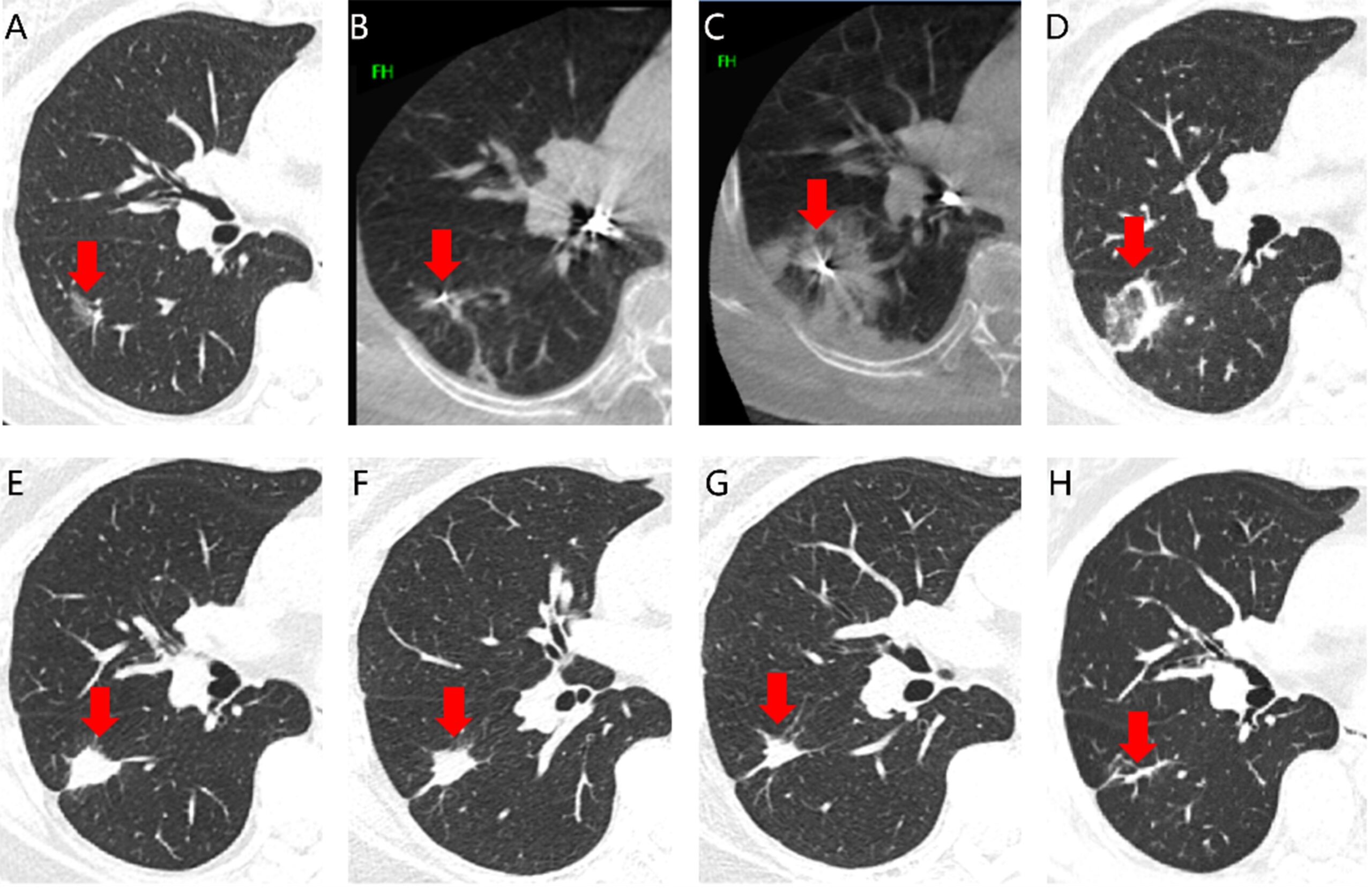
Comment by Mark Lavercombe: In this study, researchers used transbronchial radiofrequency ablation (RFA) with automatic saline microperfusion in patients with lung tumours deemed unsuitable for surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy. One hundred twenty-six patients underwent RFA on 130 lesions less than 3 centimetres in size that were accessible bronchoscopically, and 22 of those patients required a further RFA treatment at three months. After twelve months of follow-up, a complete ablation rate of 90% was achieved, which was even higher in patients with mixed density or pure ground glass lesions (97%). Although the authors considered the procedure relatively safe, one patient died of massive haemoptysis after the procedure. Further studies will be required to clarify the potential role of transbronchial RFA within the treatment armamentarium.



