
Education&ScienceEducational Article
Trajectory of Lung Function in Diabetic Adults: A 16-year Follow-up Study of Community-based Prospective Cohorts
May 2024
Authors: Wonsuk Choi, Joon Ho Moon, Hayoung Choi, Hyun Lee, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang and Nam H. Cho
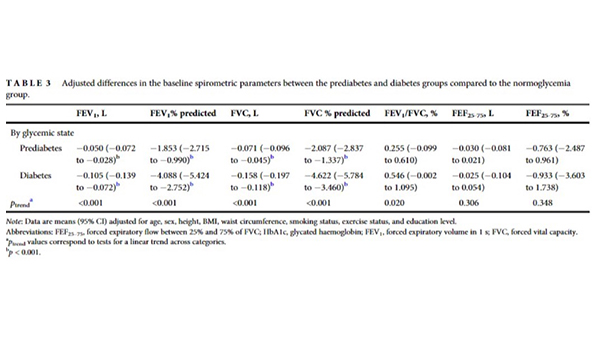
Comment by Mark Lavercombe: In an attempt to demonstrate an association between diabetes mellitus and lung function, this community cohort of 6483 middle-aged and older adults in Korea undwerwent serial lung function testing over sixteen years. At baseline, participants with diabetes had signficantly lower FEV1, FEV1 % predicted, FVC, FVC % predicted, and FEV1/FVC, even after adjustment for covariates (age, sex, height, body mass index, waist circumference, smoking status, exercise status, and education level). Longitudinal analysis shows a higher rate of decline in those with diabetes compared with those with normoglycaemia. This study strengthens the argument for an association between impaired glycaemic control and impaired lung function.



